1.1.5 Energy relations between compounds
Without describing exactly how, the MRM states that compounds consist of multiple momenta that form collective momenta. This enables compounds to have mass, relative velocities and thereby more slowly changing positions. The relations between compounds can be seen as a means of energy storage at a higher application level. Such total energies relate to the compounds internal energy Eint (mass).
Energy stored as velocity differences between compounds is termed kinetic energy and has a magnitude of Eint(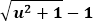 ), where u represents the proper speed between two compounds. This definition is elaborated further in section 3.7 Energy required for acceleration.
), where u represents the proper speed between two compounds. This definition is elaborated further in section 3.7 Energy required for acceleration.
Energy stored as positional differences between compounds is termed gravitational potential energy and has a magnitude of -Eint(eq - 1), where q represents the depth in a gravitational system. This definition is elaborated further in section 4.4 Energy relations in gravitational systems.