3.2 Time dilation
3.2.2 Derivation
Let us consider some examples of the magnitude of the time dilation when traveling between planets A and B at various speeds according to their frame of reference:
|
Measured velocity |
Outer travel time |
f |
Inner travel time |
% of outer time |
γigs |
|
0.25c |
40 min |
1.291 |
38.73 min |
96.8 % |
1.032 |
|
0.5c |
20 min |
1.732 |
17.32 min |
86.7 % |
1.155 |
|
0.667c |
15 min |
2.236 |
11.18 min |
74.5 % |
1.342 |
|
0.833c |
12 min |
3.317 |
6.634 min |
55.3 % |
1.809 |
|
0.99c |
10.10 min |
14.107 |
1.425 min |
14.1 % |
7.088 |
|
0.999c |
10.01 min |
44.7325 |
0.447 min |
4.47 % |
22.39 |
We can derive the time dilation factor γigs by imagining an object traveling through another frame of reference at a certain speed. The ratio of the resulting times should be calculated to determine γigs. The expansion factor will be used in this calculation.
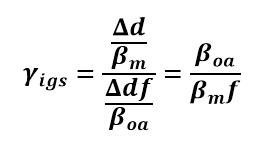
We can then insert the previously defined equations for βoa and f as functions of βm. After simplification, this equation becomes equivalent to the Lorentz factor:
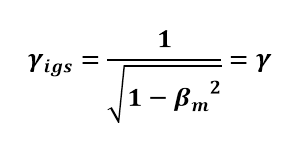
The formula for the difference in experienced time is consistent between the MRM and SR.